The vagus nerve, one of the most critical nerves in the human body, plays a pivotal role in the parasympathetic nervous system, which oversees a vast array of crucial bodily functions. Understanding the vagus nerve’s functions and the health conditions associated with it is of immense importance for medical professionals. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the vagus nerve and discuss various health conditions related to its functionality.
Anatomy and Function of the Vagus Nerve
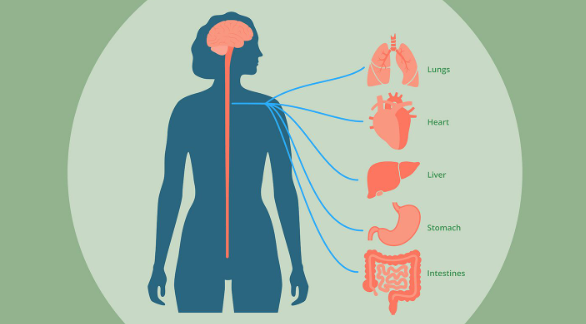
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, is the longest and most complex of the cranial nerves. It extends from the brainstem through the neck and into the abdomen, innervating various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. The primary function of the vagus nerve is to mediate the body’s parasympathetic response, often termed the ‘rest and digest’ system. It controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, respiratory rate, and digestion, and also transmits sensory information from the internal organs to the brain.
Vagus Nerve and Heart Health
One of the critical roles of the vagus nerve is regulating the cardiovascular system. It helps control heart rate and blood pressure, and an imbalance in its function can lead to conditions such as bradycardia (abnormally slow heart rate) or tachycardia (abnormally fast heart rate). Vagal nerve dysfunction can also contribute to heart rhythm disorders like atrial fibrillation, impacting overall cardiovascular health.
Gastrointestinal Effects of Vagus Nerve Dysfunction
The vagus nerve significantly influences gastrointestinal function. It regulates the movements of the digestive tract, including the process of peristalsis, which moves food through the digestive system. Disorders of the vagus nerve can lead to conditions like gastroparesis, where the stomach cannot empty properly, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Additionally, vagal nerve abnormalities can contribute to Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and other gastrointestinal disorders.
Respiratory Implications
In respiratory health, the vagus nerve plays a role in controlling the muscles involved in breathing. Dysfunction in the vagus nerve can lead to respiratory challenges, including difficulty in regulating breathing patterns. This can have implications for conditions such as sleep apnea and may exacerbate respiratory illnesses like asthma.
Vagus Nerve and Mental Health
Recent research has highlighted the vagus nerve’s role in regulating mood and stress responses. Dysfunctions in vagal nerve activity have been associated with mental health conditions like depression and anxiety. The nerve’s role in the ‘gut-brain axis’—the communication pathway between the gut and the brain—also suggests its involvement in mental health, given the emerging evidence linking gut health to psychological well-being.
Vagal Nerve Stimulation Therapy
Vagal nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy is a treatment method that involves delivering electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. This therapy has been used to treat conditions like epilepsy and depression. VNS has shown promising results in reducing the frequency of seizures in epilepsy and improving mood in treatment-resistant depression. The exploration of VNS in other conditions related to vagus nerve dysfunction is ongoing.
Impact of Lifestyle on Vagal Tone
Vagal tone, the activity level of the vagus nerve, can be influenced by various lifestyle factors. Regular exercise, stress management techniques like meditation and deep breathing exercises, and a healthy diet have been shown to improve vagal tone. Improving vagal tone can lead to better heart rate variability, a marker of cardiovascular health, and overall well-being.
Challenges in Diagnosing Vagus Nerve Disorders
Diagnosing disorders related to the vagus nerve can be challenging due to its widespread influence on the body. Symptoms of vagal nerve dysfunction can be diverse and non-specific, making accurate diagnosis complex. Healthcare professionals rely on a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and specialized tests to diagnose conditions associated with the vagus nerve.
Future Directions in Vagus Nerve Research
The vagus nerve remains a subject of extensive research, with scientists exploring its potential in treating various health conditions. The development of non-invasive vagal nerve stimulation techniques and a deeper understanding of the nerve’s role in different bodily systems are areas of ongoing study. This research holds promise for innovative treatments for a range of disorders associated with the vagus nerve.
Conclusion
The vagus nerve is a cornerstone of the parasympathetic nervous system, playing a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the human body. Its impact on heart, gastrointestinal, respiratory, and mental health illustrates its significance in overall well-being. Understanding the functions of the vagus nerve and the health conditions associated with it is crucial for medical professionals in diagnosing, treating, and managing these conditions. As research progresses, the potential for new therapies targeting the vagus nerve continues to expand, offering hope for improved treatments for various health disorders.