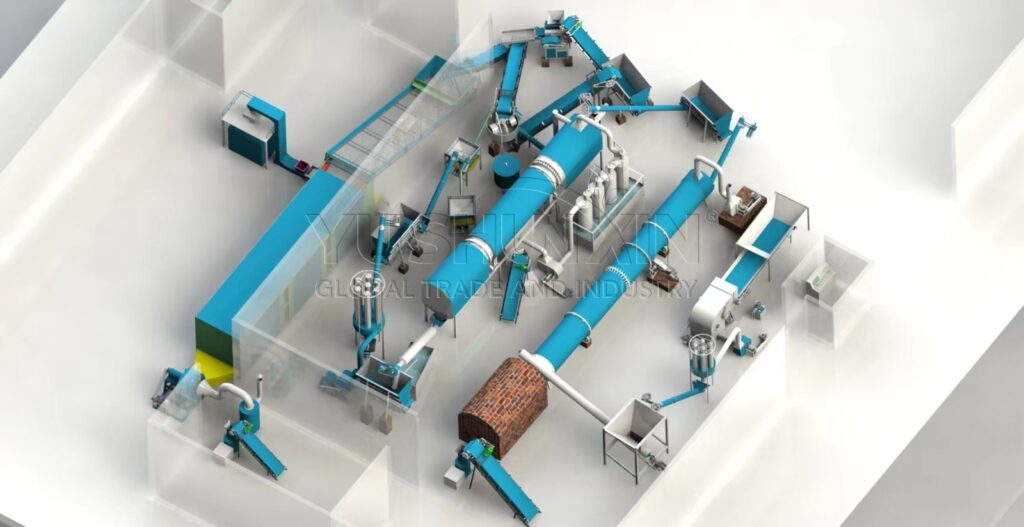
Introduction
Charcoal has been a vital energy source for centuries, used for cooking, heating, and even metallurgy. In modern times, its uses have expanded into recreational activities such as shisha (hookah) smoking, where high-quality charcoal is essential. At the same time, sustainability and efficient waste utilization have led to new ways of producing charcoal from materials that would otherwise go to waste—such as sawdust.
Today, two topics dominate conversations in this space: the shisha charcoal making machine, designed to produce consistent, high-quality briquettes for hookah use, and the process of how to make charcoal from sawdust, which turns wood industry waste into a profitable and eco-friendly product.
This comprehensive guide explores both. We’ll look at how shisha charcoal is made, what machinery is needed, the process of converting sawdust into charcoal, and how entrepreneurs can benefit from investing in these technologies.
Part I: Shisha Charcoal Making Machine
What Is a Shisha Charcoal Making Machine?
A shisha charcoal making machine is a specialized production system that converts raw biomass materials like coconut shells, fruit husks, or wood into small, uniform briquettes specifically for hookah or shisha use. These briquettes differ from regular charcoal:
- They must burn evenly.
- They should produce minimal smoke and no unpleasant odors.
- They must be compact, often shaped into cubes, hexagons, or discs.
The machine ensures that every briquette meets these criteria by applying pressure, controlled heat, and shaping molds.
Why Is It Important?
Hookah smoking is not just a pastime; it’s a cultural tradition across the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Asia, with growing popularity worldwide. With the rise of hookah lounges and shisha cafés, demand for quality shisha charcoal has surged.
A shisha charcoal production line provides:
- Consistency: Every briquette is uniform in shape and size.
- Efficiency: Machines can produce thousands of briquettes per hour.
- Profitability: Low-cost raw materials are turned into a high-value product.
How a Shisha Charcoal Production Line Works
The shisha charcoal making machine isn’t a single piece of equipment but part of a production line. Here’s the step-by-step process:
1. Carbonization of Raw Materials
Biomass like coconut shells, bamboo, or wood is carbonized in a carbonization furnace. This process burns the material in a low-oxygen environment, leaving behind pure charcoal.
2. Crushing and Grinding
The carbonized material is brittle and needs to be crushed into fine powder. A crusher or hammer mill is used here.
3. Mixing with Binder
Since charcoal powder alone doesn’t stick together, natural binders like starch or molasses are added. Water may also be added to create a pliable mixture.
4. Briquetting
The mixture is fed into a shisha charcoal briquette press machine, which compresses it under high pressure into molds. The output could be cube-shaped, hexagonal, or round briquettes depending on the mold design.
5. Drying
Freshly pressed briquettes contain moisture and must be dried, usually in a mesh belt dryer or drying oven, to reduce moisture content to less than 5%.
6. Packaging
Finally, briquettes are cooled and packed into branded bags or boxes, ready for distribution.
Key Features of Shisha Charcoal Machines
- Variety of Shapes: Cubes, rounds, or hexagons.
- High Production Capacity: From a few hundred kilograms to several tons per day.
- Automation: Reduces labor requirements.
- Durability: High-density briquettes burn longer, making them more attractive for shisha use.
Advantages of Using a Shisha Charcoal Machine
- Eco-Friendly Production: Biomass waste is repurposed.
- Cost-Effective: Raw materials are cheap, often byproducts of other industries.
- High Market Demand: Shisha charcoal sells at premium prices in global markets.
- Scalability: Machines are available for small, medium, and large-scale businesses.
Part II: How to Make Charcoal from Sawdust
Why Sawdust?
Sawdust is one of the most abundant waste products from woodworking industries. Traditionally discarded or burned, it now serves as an excellent feedstock for charcoal production. Making charcoal from sawdust is both eco-friendly and profitable.
Step-by-Step Process of Making Charcoal from Sawdust
1. Collection and Preparation
Gather sawdust from sawmills, furniture factories, or other woodworking operations. The material must be free from chemical contamination.
2. Drying
Fresh sawdust often contains high moisture (up to 50%). Drying reduces this to around 10–15% before carbonization. Dryers or natural sun-drying can be used.
3. Carbonization
The dried sawdust is loaded into a continuous carbonization furnace. In a low-oxygen environment, it is heated to 400–600°C. This process removes volatile components, leaving carbon-rich charcoal.
4. Crushing and Screening
The resulting charcoal may be lumpy and uneven. It is crushed and screened into fine powder.
5. Mixing with Binder
As with shisha charcoal, binders like starch are mixed in to form a cohesive material.
6. Briquetting
The mixture is pressed into briquettes using a charcoal briquette press machine. The size and shape can vary depending on end use: sticks, balls, cubes, or pillow-shaped briquettes.
7. Drying and Cooling
The briquettes are dried until their moisture content is under 5%, ensuring durability and better burning performance.
8. Packaging
Finally, they are packaged into bags for sale as fuel, barbecue briquettes, or for industrial use.
Advantages of Sawdust Charcoal
- Eco-Friendly: Converts waste into useful energy.
- Renewable: Unlike coal, sawdust is continuously produced.
- Clean Burning: Produces less smoke and ash.
- Cost-Efficient: Raw material is low-cost or free.
- Market Versatility: Can be used in cooking, heating, barbecuing, or soil improvement (biochar).
Applications of Sawdust Charcoal
- Household Fuel: Used in stoves and heaters.
- Barbecues: A popular choice due to its long burning time.
- Industrial Use: Smelting, blacksmithing, or metallurgy.
- Biochar for Agriculture: Improves soil fertility, water retention, and carbon sequestration.
Part III: Comparing Shisha Charcoal Machines and Sawdust Charcoal Production
| Feature | Shisha Charcoal Machine | Sawdust Charcoal Production |
|---|---|---|
| Target Market | Hookah lounges, shisha cafés, retail shops | Households, BBQ suppliers, industrial users, farmers |
| Product Type | Small, uniform briquettes (cube, round, hexagonal) | Briquettes, sticks, or bulk charcoal |
| Raw Materials | Coconut shells, bamboo, fruit husks, wood | Sawdust from woodworking |
| Value Addition | Premium, high-profit market | Versatile applications |
| Scalability | Small to medium scale | Small to large scale |
Part IV: Business Opportunities and Investment Potential
Both shisha charcoal making machines and sawdust charcoal production lines offer strong business opportunities.
Market Demand
- Shisha charcoal demand is rising globally due to cultural traditions and the growth of hookah lounges.
- Sawdust charcoal demand is high for barbecue fuel, industrial energy, and biochar markets.
Return on Investment
- Raw material costs are low.
- Equipment, though initially costly, pays off quickly due to high market demand.
- Profit margins can range from 30%–50% depending on scale.
Sustainability Benefits
- Reduces deforestation by relying on waste biomass.
- Cuts down on sawdust waste disposal issues.
- Provides a renewable, carbon-neutral fuel source.
Conclusion
The world is moving toward sustainable energy solutions, and charcoal production from biomass offers a perfect example. Whether through a shisha charcoal making machine for premium hookah briquettes or learning how to make charcoal from sawdust for versatile fuel and biochar, both approaches combine profitability with environmental responsibility.
For entrepreneurs, farmers, and manufacturers, investing in these systems means not only tapping into lucrative markets but also contributing to waste reduction and sustainability. The technology is mature, accessible, and highly scalable—making now the perfect time to get started.