Lupus, or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks healthy tissues and organs in the body. The exact cause of lupus is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors.
Causes of Lupus:
Genetic Factors:
There is a genetic predisposition to lupus, and it tends to run in families. Certain genes may increase the likelihood of developing the disease.
Environmental Triggers:
Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as sunlight, infections, certain medications, and hormones, may trigger the onset of lupus in individuals with a genetic predisposition.
Hormonal Factors:
Hormonal factors, particularly the influence of estrogen, may play a role in lupus. The disease is more common in women, and its onset or flares can be associated with hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
Symptoms of Lupus:
Lupus can affect various organs and systems in the body, leading to a wide range of symptoms. Common symptoms include:
Joint Pain and Swelling:
Lupus often causes arthritis, resulting in pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints.
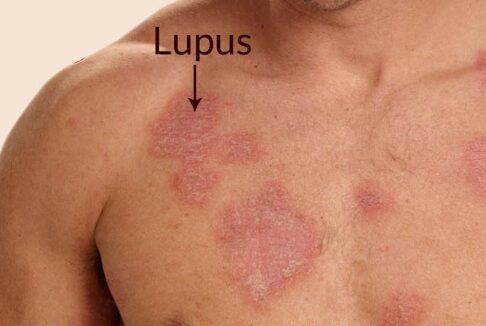
Skin Rashes:
Butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose (malar rash), as well as other skin rashes. Visit a Dermatologist in Karachi to get the appropriate treatment.
Fatigue:
Persistent and extreme fatigue is a common symptom.
Fever:
Many people with lupus experience recurrent low-grade fevers.
Photosensitivity:
Increased sensitivity to sunlight, leading to skin rash or flare-ups.
Kidney Involvement:
Lupus can affect the kidneys, leading to symptoms such as blood in the urine, increased protein in the urine, and kidney inflammation.
Chest Pain:
Inflammation of the lining of the heart or lungs may cause chest pain.
Mouth or Nose Ulcers:
Painful sores in the mouth or nose.
Neurological Symptoms:
Lupus can affect the nervous system, leading to symptoms like headaches, seizures, or cognitive difficulties.
Treatment of Lupus:
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for joint pain.
- Antimalarial drugs for skin and joint symptoms.
- Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive drugs to modulate the immune system.
Sun Protection:
Sunscreen and protective clothing are essential to manage photosensitivity.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management are important for overall health.
Close Monitoring:
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers for monitoring and adjusting treatment as needed.
Supportive Therapies:
Physical therapy and occupational therapy may be beneficial for managing symptoms.
Lupus is a complex and individualized condition, and treatment plans may vary based on the specific manifestations of the disease in each person. It’s crucial for individuals with lupus to work closely with healthcare professionals such as a Skin Specialist in Lahore to manage their symptoms effectively.